USMCA(旧NAFTA)の原産地基準のうち、価格をベースにして原産性を判断する方法に
RVC(Regional Value Content)での原産地判定という方法があります。
「製品価格のうちの○○%以上がUSMCA原産であれば製品全体を
USMCA産品とみなす」というものです。
例えばメキシコで製造された物をアメリカに輸出し
USMCAの特恵関税を適用させたいが、メキシコでの製造の際に
日本産の原料やパーツを使用した場合、どの程度の日本産の使用であれば
メキシコ産として認められるのかを価格を基準にして判断する方法が
このRVCという事になります。
USMCAにはこのRVCの計算方法が2つあり、
Transaction Value MethodとNet Cost Methodと呼びます。
この2のどちらでも計算できる場合は有利な計算方法を選択し、
原産地規則を満たす事が可能です。
Transaction Value Method
Transaction Value Methodは以下の計算式によって算出されます。
※TVはFOBベースでの製品価格
※VNMはUSMCA以外で調達した非原産材料

この方法によって算出されたRVCの値をもって原産性の有無を判定します。
後程計算例を紹介します。
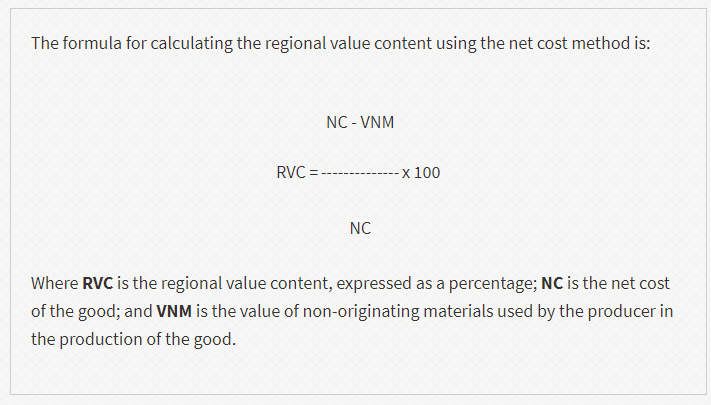
Net Cost Method
Net Cost Methodは以下の計算式によって算出されます。
※VNMはUSMCA以外で調達した非原産材料
※NCはネットコスト(ネットコストとは産品価格から経費を引いたもの
例えば広告費、マーケティング費用、アフターサービス料、ロイヤリティ
船賃、梱包、金利等)
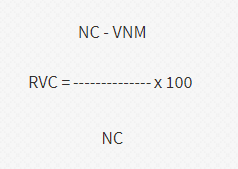
この方法によって算出されたRVCの値をもって原産性の有無を判定します。
こちらも後程計算例を紹介します。
原産地規則例
電気式ヘアーアイロン(HS:8516.32)の原産地規則の例を紹介します。
provided there is a regional value content of not less than:
(a) 60 percent where the transaction value method is used, or
(b) 50 percent where the net cost method is used.
(※一部省略)
冒頭のprovided there is a regional value content of not less thanは
RVCが以下の値を下回らない事が原則という意味になります。
そして青文字の(a) 60 percent where the transaction value method is used
というのがTransaction Value Methodを使用した計算方法で60%以上という
意味になりますので、先ほど紹介した以下の計算式で60以上になれば
原産地規則を満たすという事になります。

もう一方の赤文字の(b) 50 percent where the net cost method is used
というのがNet Cost Methodを使用した計算方法で50%以上という
意味になりますので、先ほど紹介した以下の計算式で50以上になれば
原産地規則を満たすという事になります。

原産地規則はこの2つの計算方法のどちらか一方を満たす事を条件として
おりますので、一方が満たされないのであればもう一方を検討し、
条件を満たす方を適用して、原産性を満たす事が可能です。
計算例
メキシコで製造された電気式ヘアーアイロン(HS:8516.32)は
日本から調達した日本産のヘアーカーラーパーツ(HS:8516.90)を使用している
完成品の電気式ヘアーアイロンのFOB価格は$4.40で、ネットコストは$3.90
日本から調達した日本産のヘアーカーラーパーツの価格は$1.80
Transaction Value Methodで60%とNet Cost Methodで50%のどちらかを
満たせば良いので、それぞれ計算してみます。
Transaction Value Methodで計算

上記の計算式に
TVにFOB価格の$4.40を代入
VNMに日本から調達した非原産材料価格の$1.80を代入すると
計算式は以下のようになります。
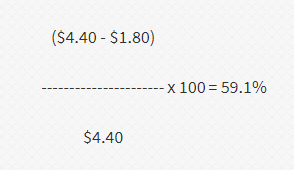
RVCは59.1%という事になり、一つ目のRVCの計算方法である
(a) 60 percent where the transaction value method is used
では原産地規則を満たさないという事になります。
Net Cost Methodで計算

上記の計算式に
NCにネットコストの$3.90を代入
VNMに日本から調達した非原産材料価格の$1.80を代入すると
計算式は以下のようになります。
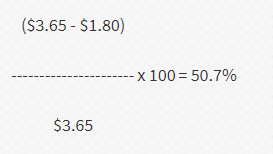
RVCは50.7%という事になり、二つ目のRVCの計算方法である
(b) 50 percent where the net cost method is used
を満たす事になります。
よって上記価格例の電気式ヘアーアイロンの原産地規則は
Net Cost Methodを用いればUSMCA原産地規則を満たすという事になり
USMCA締約国向けの輸出に関しては特恵関税が適用されるという形になります。
上記で紹介した電気式ヘアーアイロンの原産地規則は一部省略しております。
全文は以下のページで紹介しております。