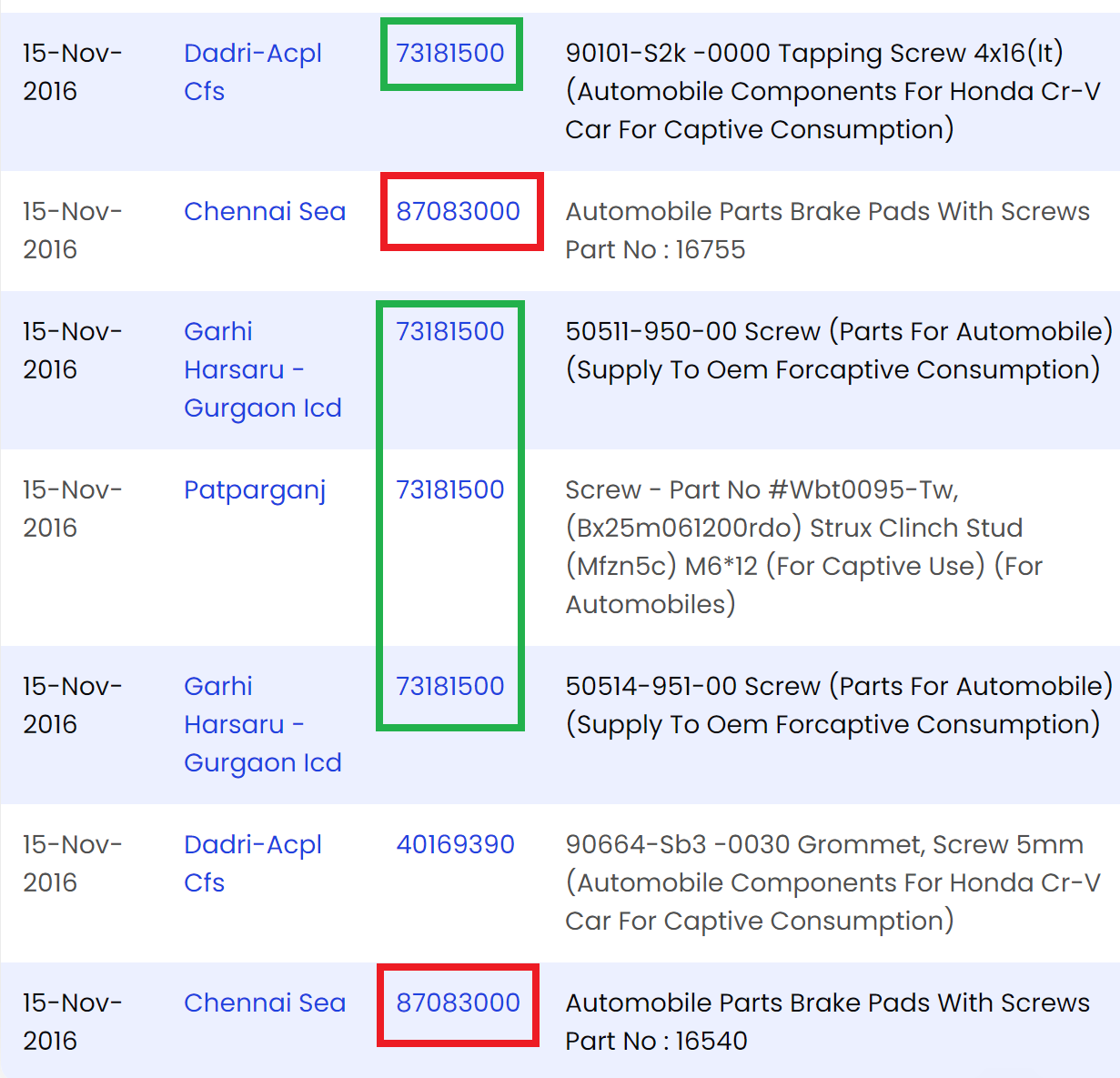
What’s the difference between “part” and “accessory” under HS code?
There is no clear definition in HS Tariff or even Explanatory note.
Instead, we can see the definition in customs ruling case of “sewing machine”.
The issue of this ruling is that whether Sewing Machine Light is “part” or “ lamp” as an accessory.
The following HS codes are under consideration:
8452.90: Sewing machines, other than book-sewing machines of heading 8440; furniture, bases and covers specially designed for sewing machines; sewing machine needles; parts thereof:
9405.40: Lamps and lighting fittings including searchlights and spotlights and parts thereof, not elsewhere specified or included; illuminated signs, illuminated nameplates and the like, having a permanently fixed light source, and parts thereof not elsewhere specified or included:

Source:European Union Website
Part
“part” of an article is something necessary to the completion of that article. It is an integral, constituent, or component part, without which the article to which it is to be joined, could not function as such article.
Source: United States v. Willoughby Camera Stores, Inc., 21 C.C.P.A. 322 (1933)
Accessory
“accessory” is not necessary to the functioning of the sewing machine but serves the subordinate purpose of illuminating the stitching area. Merchandise used in conjunction with an item in a subordinate role to the function of that item has been described as an accessory, and not as a part,
Source: the Court of International Trade. See, Rollerblade, Inc. v. United States, 116 F. Supp. 2d 1247, 1252 (Ct. Int’l Trade, 2000).
Conclusion
Sewing machine light is classified as other electric lamps and lighting fittings HS:9405.
Since the sewing machine will function even if the lamp is subsequently removed and it serves the subordinate purpose of illuminating the stitching area, it can not be classified as a part of a sewing machine.
Here quote from customs ruling case of “sewing machine”
The sewing machine light illuminates the sewing area in the same manner as any overhead or desk lamp. Although dedicated for use with a sewing machine, the sewing machine will function even if the lamp is subsequently removed. Furthermore, the instant merchandise is advertised as an “accessory” and is not necessary to the functioning of the sewing machine but serves the subordinate purpose of illuminating the stitching area. Merchandise used in conjunction with an item in a subordinate role to the function of that item has been described as an accessory, and not as a part, by the Court of International Trade. See, Rollerblade, Inc. v. United States, 116 F. Supp. 2d 1247, 1252 (Ct. Int’l Trade, 2000).