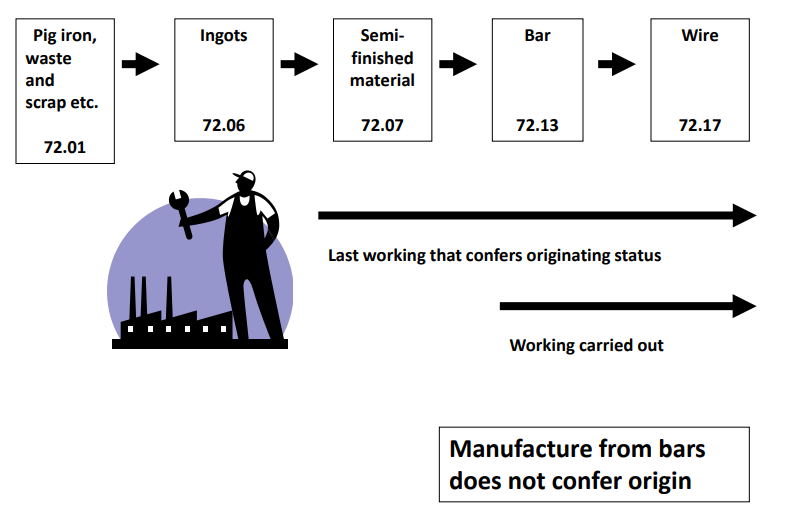
Here is a case study of “CTC” & “VA” method combined pattern.
Company A manufactures Industrial fans (HS Heading 84.14)

Industrial fans of heading 84.14 are manufactured from the
following non-originating materials:
| Final product | non-originating materials |
HS code | Value |
|
Industrial fans
|
Fan hub | 84.14 | € 14.- |
| Motor | 85.01 | € 40.- | |
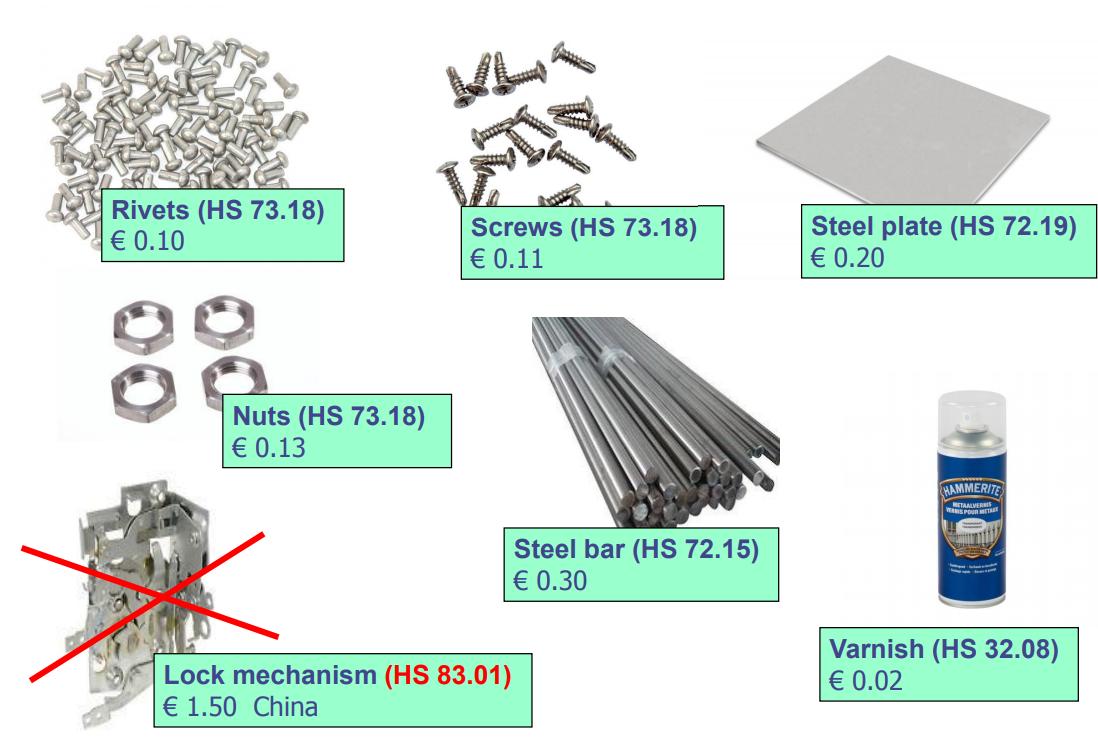
| Bolts | 73.18 | € 20.- |
Example PSR for goods of heading 84.14 (Industrial fans ) is:

*This rule (PSR) varies depending on the agreement
There are two alternative rules:
Either of them need to be fulfilled in order to be considered as originating goods.
The first condition (Column 4)
“Manufacture in which the value of all the materials used does not
exceed 25 % of the ex-works price of the product”.
This condition is not satisfied since the total value of the non-originating
material used is 74 € which means 37 % of the ex-works price of one fan (200 €).
The second condition (Column 3)
“Manufacture:
• from materials of any heading, except that of the product, and
• in which the value of all the materials used does not exceed 40 % of the ex-works
price of the product”.
This rule contains 2 conditions which must be satisfied.
(i) The change of tariff requirement of the first part of the rule is not satisfied for
the fan hub(84.14).
The general tolerance rule allowing the use of non-originating material, provided
that their value does not exceed 10 % of the ex-works price (fun hub 14 € versus
value of the final (200 €) can help to fulfill the requirement.
The limitation in the general tolerance rule saying that any of the percentages
given in the list for the maximum value of non-originating materials must not be
exceeded through the application of the general tolerance rule is also fulfilled.
(ii) The second condition in column 3 is that the total value of the non-originating
materials used must not exceed 40 % of the ex-works price of the product. This
condition is also fulfilled as the total value of the non-originating materials used is
only 37 % of the ex-works price of the fan.
The fans are considered as originating products.

 *This rule (PSR) varies depending on the agreement
*This rule (PSR) varies depending on the agreement